Strategic technologies for Sweden
Analysis basis 2025

Strategic technologies for Sweden
Go directly to the reportHow competitive is Sweden in strategically important technology areas? In this year's analysis, Vinnova provides an overview of global trends, Sweden's position and how different technology areas interact. The analysis has been developed to provide knowledge to support national priorities.
An English version of the report will be published in early 2026
The race to lead the development of key technologies and raw materials is rapidly intensifying. In 2025, competition has increased further, with the US, China and the EU at the forefront. This technology competition is a central part of the large and unpredictable changes that are shaking the world. The changes can cause systemic crises, break up value chains and create new alliances. This affects value creation, national security and leadership in technology development. The hunt for technical expertise is also becoming increasingly intense.
Global investments in research and development has slowed after decades growth, due to reduced public spending. The development is explained by the recession, high interest rates, inflation and geopolitical tensions. At the same time, corporate investment, which accounts for the majority of investments in research and development in the US, China and OECD countries, is increasing.
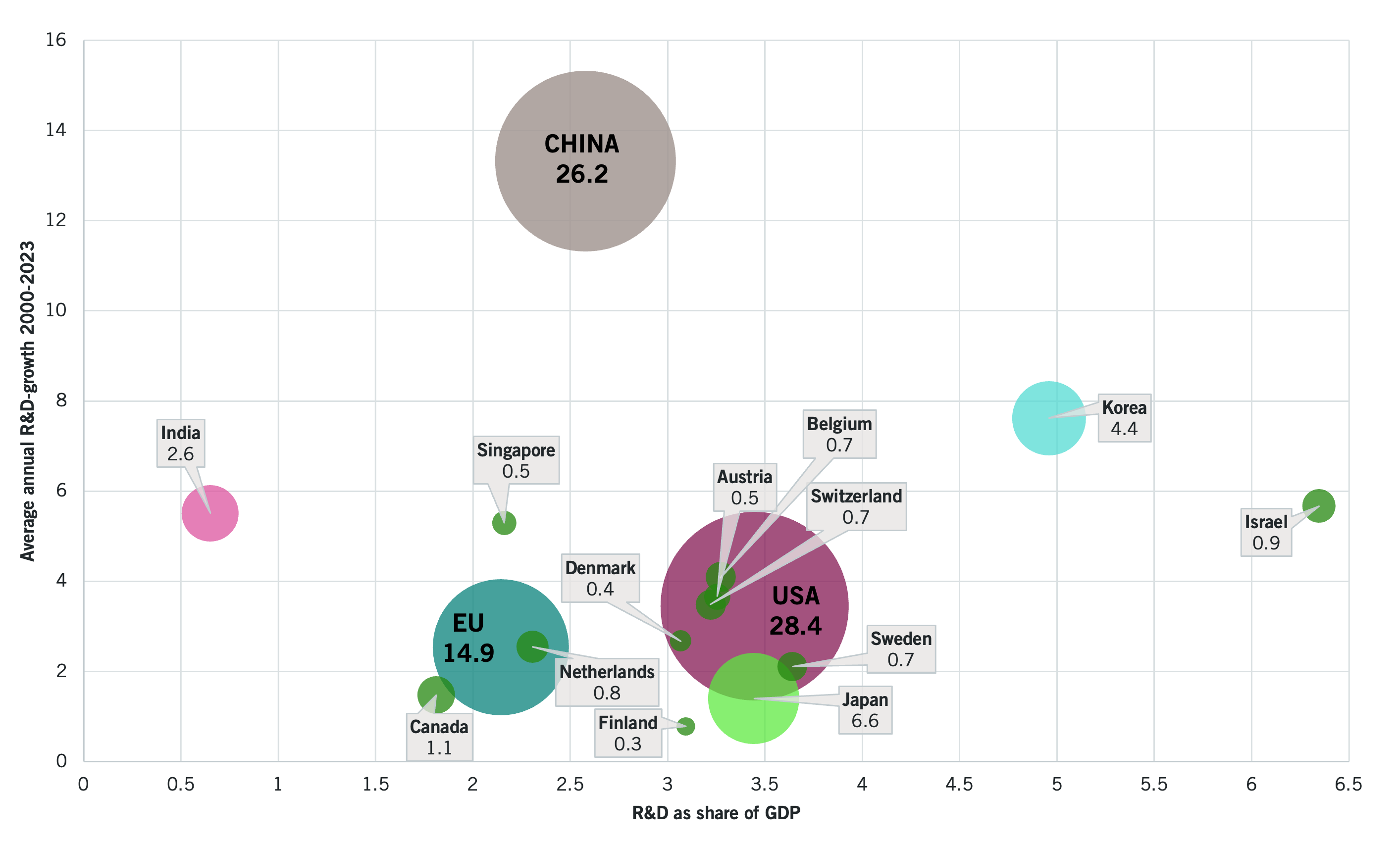
Global R&D investments has slowed down – the growth rate fell from 3.6% (2022) to 2.4% (2023). Public R&D budgets decreased by about 1.2% in real terms between 2023 and 2024. At the same time, business R&D investments has increased in OECD countries. The business sector accounts for about 78% of investment in the US and China. I EU says the average is 66% and for the OECD it is 74%.
Technological capability – a strategic resource
As developments contribute to the replacement of the previously open globalization by regionalization, technological capability becomes an important strategic resource. Despite increasing tensions, countries and research systems remain interdependent.
– Technological developments are changing the conditions for research, innovation and opportunities to address urgent challenges worldwide. Many countries are now investing heavily. For Sweden to be competitive and benefit from developments, we need to prioritize and ensure Swedish technology leadership in areas of importance. Leadership that drives excellence and innovative capacity in an international context characterized by high competition and speed is what we need, and this investment opens the way for that, says Darja Isaksson, director general of Vinnova.
Technology convergence – when different technologies are connected and used together to create new solutions – has accelerated and is now a crucial trend driving innovation and industrial applications. AI and data are the dominant force and act as a common enabler for all other areas. Combinations such as quantum technology with advanced computing, biotechnology with AI, and new materials with energy systems are examples of technology convergence with great future potential.
Sweden's technical strengths and future cooperation
Sweden is a small research and innovation country in global comparison and therefore cannot be a leader in all areas of technology. However, Sweden has strengths in several sub-areas – in some cases among the best in the world. These strengths are often linked to industrial value chains where research, innovation and production interact. This gives Sweden a competitive advantage and great development potential.
Sweden's limited size makes the country dependent on international cooperation. The EU plays a crucial role in ensuring that investments in research and innovation have the greatest possible impact. Cooperation within NATO and with countries in Asia, Canada and the UK also creates new opportunities. As many countries seek alternatives to the US and China, there is great potential for broader cooperation. Sweden also has a business sector with many internationally leading companies that are strongly interconnected in global value chains. This gives the Swedish innovation system a strength that few smaller countries can match.
Can Sweden take a leadership role in strategic technologies?
Sweden's strengths are more relevant than ever. Sweden has strong systems understanding, advanced industry and a unique ability to collaborate across technology areas. Collaboration between companies, sectors and research environments is unusually high. Sweden has test and demonstration environments that are of international top class. Competence in energy, materials and digitalisation is strong, as is a tradition of working with ethics and gender equality.
– There are good conditions to take a competitive role in the development of global technology convergences. To take an international leadership role requires pace, coordination and the ability to scale up from research to industrial production, says Göran Marklund, Vinnova's head of division for strategic analysis.
Analysis of future technology areas on behalf of the government
Vinnova has been commissioned by the government to annually monitor and analyze developments in strategically important technologies for Sweden. This report is the first update of the knowledge base that was produced in 2024. The aim is to make it easier to understand global technology developments and Sweden's international position in technology areas that are important for sustainable growth and national security.
The analysis is based on quantitative data and qualitative insights from dialogues with companies, industry organizations, universities, researchers and other actors.
More about strategically important technologies
Analysis of strategic technologies for Sweden
Recorded seminar Dec 16 on the focus on clusters of excellence and strategic technologies
Download the report
The Strategic Technologies for Sweden Report - Analysis Baseline 2025 (In Swedish)
An English version of the report will be published in early 2026
- Published
- 2025-December
- Series number
- VR 2025:12
- Publisher
- Vinnova - Sveriges innovationsmyndighet
- Author
- Liselott Bergman, Ann-Mari Fineman, Karl Hallding, Daniel Johansson, Nannan Lundin, Annika Zika-Viktorsson, Göran Marklund
- ISBN
- 978-91-89905-37-5
- ISSN
- Number of pages
- 166
Last updated 16 December 2025

